

Formal business reports are official documents that guide and inform stakeholders. These reports are valuable tools when solving company problems or making decisions.
You should be clear and include all relevant information to make your report useful in decision-making and problem-solving.
Here are five steps for writing a formal business report:
Keep reading to get valuable details under every step and learn to segment your report.
But first, let’s delve deep into formal business reports, the different types, and what differentiates them. We’ll also discuss the elements of a business report and cover valuable tips to perfect your writing skills.
Let’s get started!
Business reports provide an analysis of the current performance of a business and offer recommended actions to improve operations. A formal business report should include detailed data, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
A formal business report is a detailed and organized document that provides information about a specific topic, like research findings, market trends, or a financial situation. It usually includes conclusions based on data collected during the research process.
Formal business reports can present complicated topics in an easy-to-understand format, allowing company executives to make informed decisions. A formal report typically includes an introduction, a body of information, and a conclusion. It should consist of accurate data and reliable sources and be written formally with proper grammar and spelling.
An informal business report does not follow traditional, formal reports’ formal structure and layout. Instead, it is written in an easy-to-understand language and typically includes summaries of key points, along with recommendations or suggestions for further action.
Unlike formal reports, informal business reports do not need to be approved by higher management and can be sent directly to the intended recipient. Businesses often use informal reports to quickly provide updates or summaries of projects, data, or other important information. They are also commonly used when sharing ideas, solutions, or findings that don’t necessarily require a formal response from the receiver.
While informal reports may need more depth and detail than formal reports, they can still communicate important information concisely and clearly.
Formal business reports include different types that may be used to present data, analyze performance, or make recommendations. Examples of formal business reports include annual, research, feasibility, and marketing research reports.
Feasibility Reports
A feasibility report is an analytical document that outlines whether an activity or project has the potential to be successful. It includes cost estimates, expected outcomes, and other factors affecting the project’s success.
Business Plans
A business plan is a formal outline of a company’s objectives and strategies for achieving them. It is used to obtain financing, attract investors, and set goals for the company.
Business plans typically include sections on market analysis, organizational structure, competitive analysis, product or service description, financial projections, marketing strategies, and tactics.
Progress Reports
A progress report is a document that details the current status of a project or activity. It outlines the progress made, challenges encountered, and a timeline for when the project should be completed.
Financial Reports
Financial reports provide information about the company’s financial performance over some time. They include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Proposals
A proposal is a document that outlines how an organization, company, or individual intends to complete a project. It usually includes information such as the purpose of the project, expected outcomes, methods, and associated costs. For example, businesses may use proposals to solicit funding from investors or government agencies.
Market Research Reports
A market research report is a document that provides information about customer needs and competitor activities to develop strategies for the organization. They typically include data on consumer preferences, product demand, market trends, and other relevant factors.
Risk Reports
A risk report is a document that details the potential risks associated with a specific activity or investment. It outlines possible losses and considers how they could affect an organization’s operations. Risk reports may also include measures the organization can take to mitigate losses and recommendations for further actions.
Technical Reports
Technical reports are documents that explain the results of a technical project or investigation in detail. They are used to document the findings of a project and provide a record that can be used as reference material.
Technical reports typically include sections on research methods, results, conclusions, recommendations, and implementation plans.
Business reports inform a decision or provide direction in the form of recommendations. They may include factual data and analysis but are often practical and focus on the actionable steps needed to achieve a goal.
Academic reports take a more analytical approach, emphasizing research and thought-provoking discussions that examine different points of view.
Sources used
When writing business reports, only use real-world sources such as government reports. But when writing academic reports, you may cite theoretical works.
Conciseness
When writing business reports, use concise points with stakeholders in mind. As for academic reports, you may use technical terms and lengthy explanations to support a point.
Academic reports are often longer and more detailed than business reports and may also include recommendations but with a focus on developing new strategies or ideas.
Structure
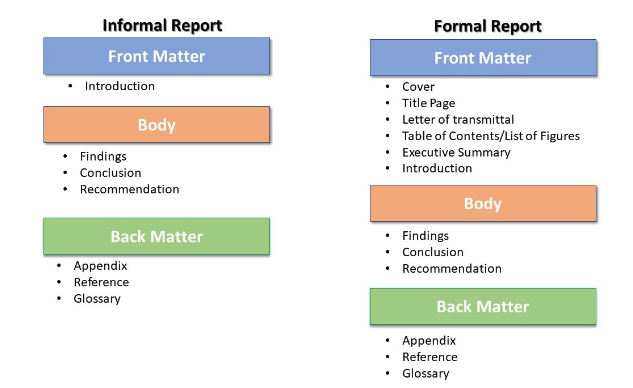
When writing a business report, adhere to the following structure: cover page, table of contents, list of figures, executive summary, introduction, body, conclusion, and recommendations.
But when writing an academic report, follow the structure: introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The purpose of both types of reports is to provide information that is useful and relevant to the target audience. So keep the audience in mind when writing a report; what information do they need to know? How will it help them make decisions or understand a concept better?
An excellent formal business report organizes information into these sections:
The title page indicates the company name (and logo), the author’s and readers’ names and positions, and the date.
The table of contents lists the sections of a report with their page number and helps jump to a specific title.

The list mentions every chart or diagram included in the report and its page number for easy navigation.

The executive summary briefly overviews the report’s key points, findings, and conclusions. It helps readers to understand the report’s data without reading the entire document. Therefore, this section should be the last to write since the facts in the report will form the executive summary.

The introduction outlines the research objectives and methods used to generate data for analysis. It sets the stage for what follows. Unlike the executive summary, it does not mention any conclusion or recommendation.

The body contains an in-depth review of the research results and their implications. It may include an analysis of trends, correlations, pictorial evidence, and other data supporting the report’s conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the data discussed in the body. It is a brief sentence that takes around three to six sentences.
The recommendation suggests an action based on the facts presented in the report. It outlines steps or policy changes necessary to solve a problem.
The appendix contains information that supports your report but would be distracting if you included it in the body. This information may consist of raw data, charts, transcripts, and surveys used for analysis or any additional resources used in the research process. You may also include acronyms used in the report.

This section consists of all references you used in your report. Citations protect you from plagiarism and give credit to your sources. You can write citations in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles, depending on the style of your formal report.
The glossary is where you define all technical terms used in the report. Use an asterisk next to words you will describe in the glossary to indicate that the reader should check the glossary for a definition.

When writing a formal business report, start by defining the purpose of the report and the intended audience. You then gather data and analyze it before writing the report. Finally, write the report and revise it accordingly.
Why are you writing the report? Consider what information you need to include and who will read the report. This will help you structure your document correctly and provide relevant information.
Defining your target audience will help you tailor the language used and choose relevant information to include in the report.
Collect all data relevant to achieving the goal of your report. This should include quantitative and qualitative data, such as customer satisfaction surveys, case studies, performance metrics, or feedback from stakeholders.
Once you have collected all of your data, analyze it and identify any trends or patterns that may be useful in writing the report. You can use various tools and techniques like statistical analysis, gap analysis, or cause-and-effect diagrams.
An outline will help you organize your research data, stay on topic, and avoid including unrelated information under a particular title. Besides having a section of each formal business report element above, outline your key points, headings, and subheadings.
Use self-explanatory headings, for example, “Impact of expanding market share.”
Organize the data you collected during research into the draft report. Start by introducing the topic, providing background information, and the report’s objectives. Then include each of the main points you want to discuss, supported by evidence from the research data.
Have the relevant elements mentioned above and write adequate information under each section. The draft does not have to be perfect; you just need to organize the data roughly.
After completing your draft, proofread and edit it to remove irrelevant data or add forgotten information. Make sure everything looks good, including the formatting. It also helps to share the business report with someone who can review it and propose necessary changes. Once everything is settled, share the report with your intended audience.
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience’s background knowledge.
Credible sources strengthen your report because they are factual, unbiased, and reliable. To identify a credible source, look out for the following markers.
Use diagrams like graphs and charts to illustrate relationships between ideas. They are more engaging, easier to understand, and they capture your audience’s attention.
Mind that you don’t clutter your diagrams with too much information. Excess detail will confuse your readers.
Achieve simplicity by:
A consistent format makes it easy to follow your report. Keep the format headings and subheadings uniform throughout your report. And make your page margins and font styles consistent.
Bold fonts stand out against regular text to draw focus on essential data and make it easier to skim through the report. Use bolding sparingly; otherwise, the effect of highlighting will not work.
A formal business report template will save both time and energy by providing a framework that simplifies the process of assembling data into a comprehensive document.
Check out this collection of editable business report templates to find one that works for you.
Formal business reports are essential tools for any business. An excellent report drives company decisions and recommends solutions to company problems. Writing one may be challenging, but this guide gives you a clear pathway to ease the process.
Remember to use visual aids and credible sources to fortify your report. Organize data into the above sections, and use the discussed tips to write your business report like a pro!
You may also like:
Join over 540,000+ happy users writing smarter with WriterBuddy. Try WriterBuddy for Free!
Advanced AI writing tool trained to write better content faster.